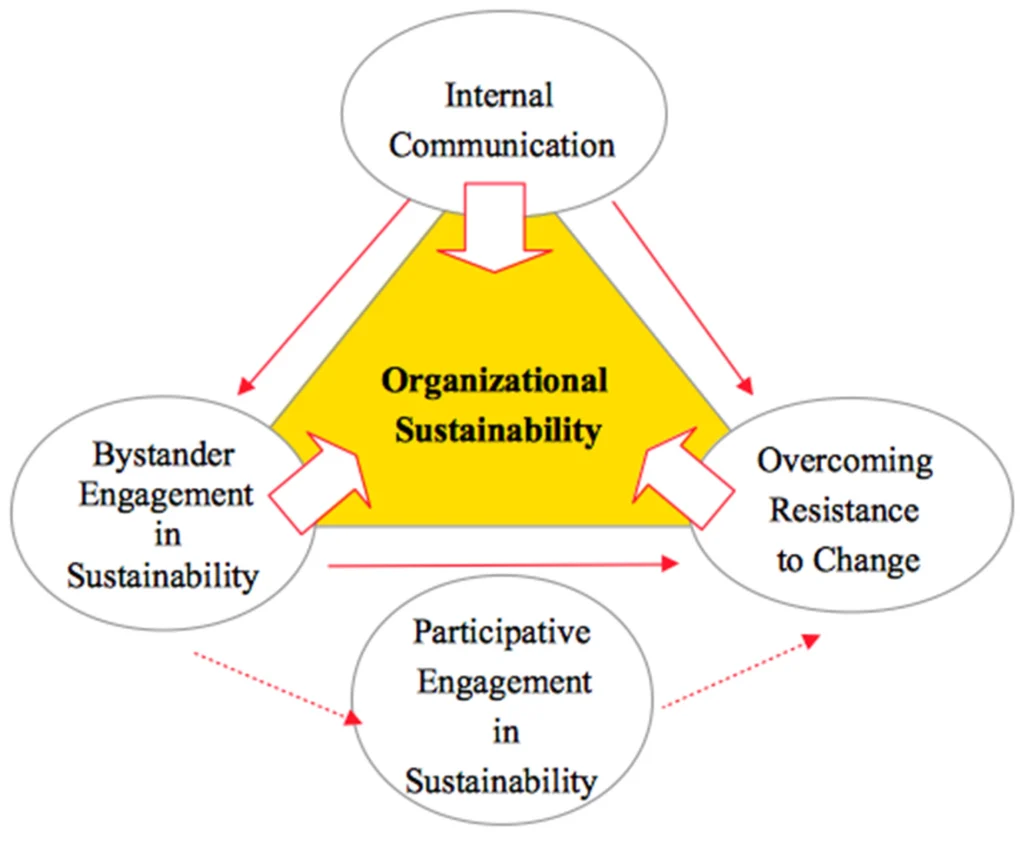
Implementing sustainabilty in organizations - The main benefits
Sustainability can benefit organizations in a variety of ways:
1. Cost savings:
Sustainability programs can assist firms in reducing their energy, water, and material usage, which can result in long-term cost savings. Investing in energy-efficient equipment, for example, can reduce energy expenses, while minimizing water usage can result in lower water bills. Cost savings can assist businesses in becoming more financially solid and robust.
2. Improved brand reputation:
As consumers and investors become more concerned about environmental and social issues, firms that embrace sustainability can strengthen their reputation among stakeholders. A positive brand reputation can result in enhanced consumer loyalty, increased employee morale, and improved relationships with suppliers and other stakeholders.
3. Innovation and competitiveness:
4. Employee engagement and retention:
Employees are increasingly seeking out employers that prioritize sustainability and social responsibility. By demonstrating a commitment to sustainability, organizations can attract and retain talented employees who share these values. This can lead to higher employee engagement, productivity, and satisfaction.
To conclude,
Sustainability can improve the well-being of organizations by driving cost savings, enhancing their brand reputation, ensuring regulatory compliance, fostering innovation and competitiveness, and improving employee engagement and retention.
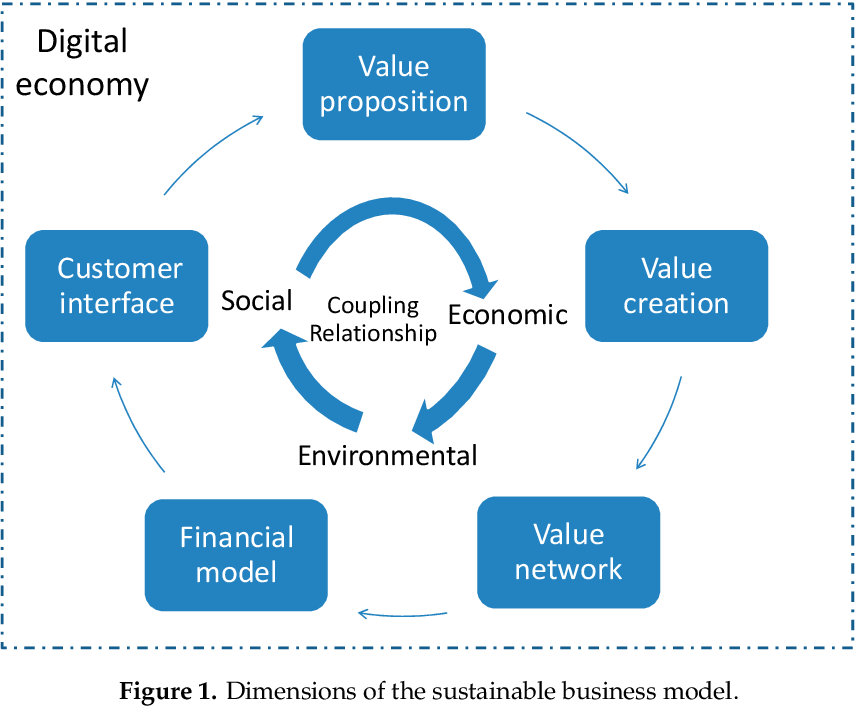
Implementing sustainability in platform and networked businesses - The main benefits
Sustainability can benefit platform and networked businesses in numerous ways:
1. Efficiency of resources:
Platform and networked businesses rely on digital technologies to facilitate user transactions and interactions. These companies can lower their energy use and carbon impact by optimizing their digital infrastructure. They can, for example, use renewable energy sources, energy-efficient servers, and efficient cooling systems in their data centers.
2. Circular economy:
Platform and networked firms can play a role in advancing circular economy principles such as waste reduction and resource optimization. They can, for example, encourage users to recycle and reuse products, or they can promote the sharing economy model, which allows users to access goods and services without owning them.
3. Social impact:
Platforms and networked businesses can leverage their reach and influence to promote and address social causes and challenges. They can, for example, collaborate with non-profit organizations to assist social and environmental efforts, or they can implement inclusive policies that promote diversity and equality.
4. Collaboration:
Platform and networked businesses can work together to exchange best practices and create industry-wide change. They can, for example, join industry alliances to promote sustainable practices and standards, or they can collaborate with supply chain partners to lessen their overall environmental effect.
5. Innovation and competitiveness:
Sustainability can fuel innovation and help platform and networked firms stay ahead of their competitors. For example, they can design new features and functions that encourage sustainability and social impact, or they can cooperate with other businesses and organizations to create new business models that address social and environmental challenges.
To conclude,
Overall, sustainability can improve the well-being of platform and networked businesses by promoting circular economy principles, addressing social issues, fostering collaboration, driving innovation and competitiveness, and attracting environmentally and socially conscious users and stakeholders.
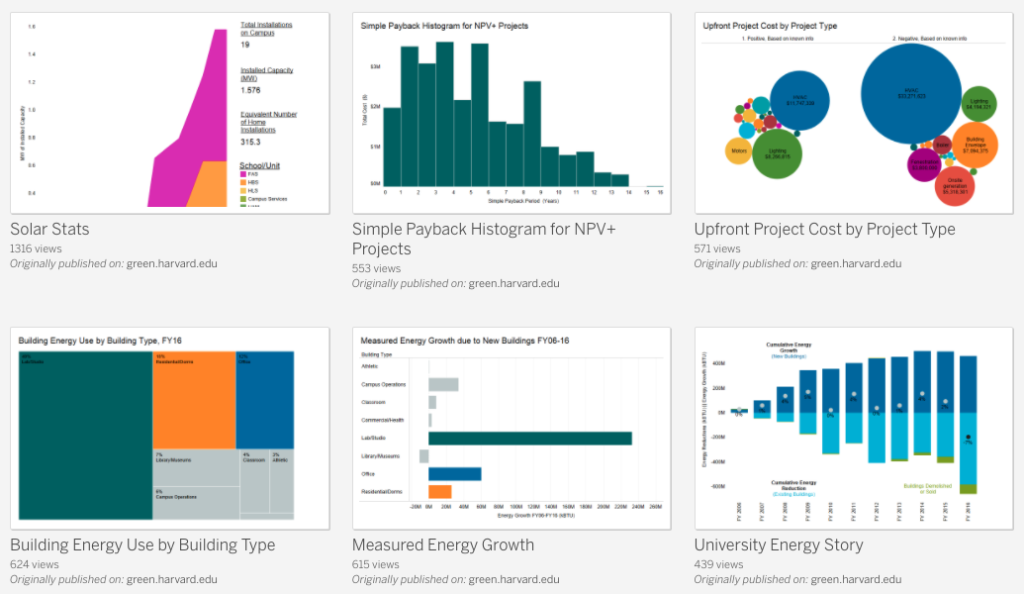
Measuring and using analytics in a sustanability context
Analytics can be an effective tool for monitoring and improving sustainability in a variety of settings.
Here are some examples of how analytics can be utilized in the context of sustainability:
1. Environmental Impact Assessment:
Analytics can be used to examine an organization’s, product’s, or service’s environmental impact. Organizations can identify areas for improvement and set targets for decreasing their environmental effect by examining data on energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and trash generation.
2. Life Cycle Assessment:
Analytics can be used to undertake a life cycle assessment of products and services, which can help discover ways to lessen their environmental impact throughout their life cycle. Organizations can identify hotspots and develop plans for decreasing their environmental effect by examining data on raw material extraction, manufacturing, transportation, consumption, and disposal.
3. Supply Chain Management:
Analytics can be used to analyze and improve supply chain sustainability. Organizations can identify high-risk suppliers and engage with them to improve their environmental and social policies by examining data on supplier performance.
4. Energy Management:
Analytics can be utilized to optimize energy consumption and lower energy costs. Organizations can find areas for improvement, such as energy-efficient equipment, lighting, and HVAC systems, by examining data on energy consumption.
5. Sustainability Reporting:
Analytics can be used to track and report on sustainability performance. Organizations can generate complete sustainability reports that demonstrate their commitment to sustainability by analyzing data on sustainability indicators such as carbon emissions, water usage, and trash generation.
To conclude,
Analytics may assist firms in identifying opportunities to enhance their sustainability performance, setting goals and tracking progress, and communicating their efforts to stakeholders.